What Is Browser Fingerprinting and How Is It Used for Tracking? | Onlinesim
- Nov 29, 2022, 12:12 PM
- 10 minutes
Many people try to avoid online spying using VPNs, proxies, or the TOR Browser. They think changing IP addresses will hide their internet activity from advertisers, governments, and hackers. However, there are other ways to track users on the Internet, such as cookies, JavaScript, and browser fingerprinting.
The fifth article from the cybersecurity series will tell you what browser fingerprinting is and how it is used for tracking.
What Is a Browser Fingerprint?
Browser fingerprint is a piece of device information collected every time a person goes online. Browser fingerprinting is called so because it is unique just like people's fingerprints.
For example, online stores can raise prices if fingerprints show that you live in a wealthy neighborhood.
A fingerprint consists of different setting parameters, from OS language to emoji type. It contains information about the operation system, the amount of RAM, and other technical characteristics.
If you want to know the uniqueness level of your PC and browser, go to the sites amiunique, coveryourtracks, deviceinfo. You will see the following information:

What Information Do Browser Fingerprints Collect?
User-agent. User-agent is a data string that lets servers identify the browser version, operational system, device type, language, toolbars, and other characteristics of the user's PC.
Time zone. Fingerprinting data about your time zone can help websites identify you.
Screen resolution and color depth. It is another setting parameter that gives the browser access to additional information about the user's device.
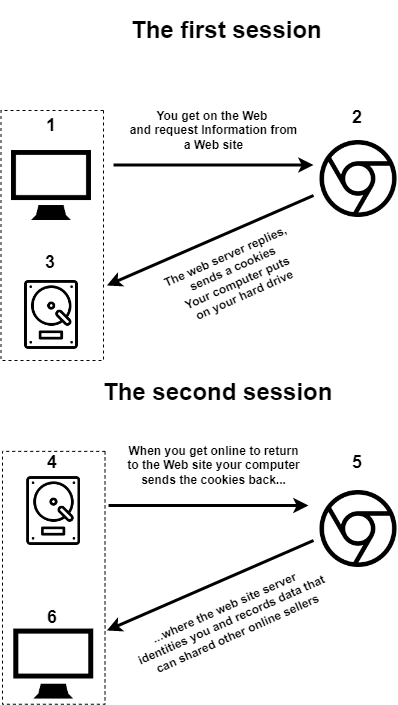
Cookies settings. Cookies are files that store information about your interaction with websites while browsing the Web.
Read more about cookies in our other article.
Supercookies. Unlike regular cookies, you cannot get rid of supercookies. They collect information even in private mode. Sometimes users are not aware that their information is stored.
System fonts, browsing history, browser plugins and their versions. This information creates an accurate portrait of the user.
How Is a Browser Fingerprint Generated?
The browser share information with servers when a person visits websites. You cannot assign an identifier to a person, but you can assign it to their browser, creating a unique code (e.g., dt4berfm59rm99j3fjecddmsk)/.
The server remembers the users’ browsers, behavior, and preferences using this code. This unique code is linked to all your online activity.
For instance, if a person logs into a social network containing personal information, a server will link it to their identifier.
Why Do Servers Use Fingerprints?
To make sure that a website opens the correct version. For example, when you access a website from your phone, a mobile-optimized version will be activated.
To make sure that a specific person visits a website. For example, if banks determine by a fingerprint that a specific person is logging into an account, they will not request confirmation via SMS or email.
To identify fraudsters. For instance, a bank can detect someone trying to log into your account from a new location or simultaneously from several locations. The bank will ask you to verify your identity, so the fraudster will not be able to steal money.
Besides, fingerprints can help to track down fraudsters, find out the characteristicsof their PC, and then their location.
To identify botnets. A botnet is a network of computers infected by malware. They can be used to perform DDoS attacks, steal bank card information and hack internet networks. Fingerprints allow you to track and block suspicious activities.
To detect VPNs and Proxies. VPNs and Proxies change your IP and location, but all the other setting parameters, such as cookies, technical specifications, and time zone, remain the same. Due to the mismatch between the setting parameters, a server can determine that a person uses anonymizers and reveal his actual fingerprint.
To collect information for advertisers. Browser fingerprint technology helps to serve accurate targeted ads. For example, iPad owners will see ads for cases for a specific model, and PC users will be shown ads for the computer's components or programs.
Does a Vpn Prevent Browser Fingerprinting?
No, VPN does not protect you against browser fingerprinting because it only changes IP and location. A VPN makes it more difficult for servers to monitor your traffic but does not entirely eliminate online spying. A portion of the user's information still ends up on the Internet.
How Do Websites Collect Browser Fingerprint Information?
Browser fingerprints are collected on two sides: server side and userside.
Server Side
Site access logs. They collect protocols, URLs, IP addresses, and User-agent.
Headers. Headers include information about the request and the client who is looking for the site. For example, headers show a website what device the client uses.
Types of headers:
- The HTTPConnection header determines whether the connection to the web page is open or whether it should be closed.
- The Accept-Languagerequest HTTPheader determines the client's systemlanguage.
- The User-Agent request header contains information about your web browser name and operating system.
- The Referer HTTP request headeridentifies the previous web page address the request was made from.
- The Cache-Control HTTP header indicated how to cache data on server side and user side.
- The HTTP Accept request header shows the site which content type the client's browser and computer can understand.
Cookies. Cookies help personalize ads but make users less anonymous.
Canvas Fingerprinting. This technique works with the HTML5 canvas element that WebGL uses to render interactive 2D and 3D graphics in the browser.
Canvas Fingerprinting forcesyour browser to display graphic content: images, texts, or their combination. But rendered graphic content is different for every browser since devices have different fonts, compression, and others.
Then canvas fingerprints turn the graphic into a hash that has a unique code. The servers learn the following information about your device through this code:
- Graphics cardtype;
- Display drivers;
- CPU (if there is no an integrated graphics card);
- Installed fonts
User Side
Adobe Flash & JavaScript. They collect information about time zone, OS version, screen resolution, and fonts used.
Cookies. Servers collect information about the user's device and their preferences using cookies. Even if do not accept cookies, some fingerprints such as user-agent, IP, and URL will still end up on the Internet.
Cross-browser fingerprinting
You will not avoid surveillance and fingerprinting using several browsers. The researchers of the System Security Lab at Johns Hopkins University have learned to track users across different browsers. They utilize information about the OS, graphics card, CPU, and other PC features.
Their approach can identify 99.24% of users. You can see this code on GitHub.
Is Browser Fingerprinting Legal?
There are no laws against gatheringcustomer information. TheGDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)and ePD (ePrivacy Directive) regulations state that fingerprint collection is not illegal. But websites need users' consent to collect information.
There are two exceptions to obtaining consent:
- The information collected during fingerprinting is required to convey a message through an electronic communication network.
- Browser fingerprints are used to customize the user interface on a specific device. For example, when a website redirects you to its mobile-optimized version.
How to Protect Yourself Against Fingerprints?
Use Firefox. Firefox browser blocks third-party requests that fingerprint. Firefox does not give servers access to device properties using JavaScript. It also hides the information gathered through network requests: IP, headers, and User-agent.
Firefox collaborates with Disconnect to provide fingerprint protection and develops script blocking and API-level protection software.
*The Disconnect company maintains alist of companies participating in cross-site tracking and fingerprint users.
webgl.disabled protects you against canvas fingerprinting. Set the True value to enable it.
geo.enabled blocks geolocation tracking. Set the False value to disable it.privacy.resistFingerprinting is another browser fingerprint protection preference. Set the True value to enable it.
privacy.firstparty.isolate isolates cookies from its own domains. Set the True value.
media.peerconnection.enabled prevents IP leakage if you use a VPN service. Set the False value.
Warning! Some site functions will not be available after disabling these preferences.
For instance, websites may not display correctly or work without WebGL. Examples of such sites are online stores with 3D graphics, like online car dealerships, where you can view 3D models of cars.
But websites will not be able to show you the correct delivery amount without geolocation enabled.
Use Brave. It is another browser with anti-surveillance protection. It blocks cross-site tracking and some scripts and upgrades connectionsto HTTPS. There is also an additional feature in the settings — disable fingerprinting.
Use extensions. Extensions help to replace your fingerprint with another.
- AdBlock Plus blocks ads, banners, and popups and disables some tracking scripts.
- uBlock Origin works like the previous one but has a more flexible configuration. You can find an additional filter on GitHub.
- ScriptSafe blocks Java, JavaScript, and Flash on web pages.
- Ghostery blocks cookie and script tracking. You can configure which tracking parameters to block in the settings.
- Privacy Badgerprotects against trackers that are loaded on websites.
- Chameleon changes user-agent values and allows setting them to change periodically(e.g., every 10 minutes).
- AbsoluteDoubleTrace protects against browser fingerprinting techniques.
- User-Agent Switcher changes user-agent information.
Disable JavaScript. Servers use JavaScript to collect information about users. But you can disable it in the settings.
- Firefox. Type "about:config" in the address bar and accept the risks. In the new address bar, type "javascript.enabled" and set it to false.
- Chrome. Go to the settings and type "JavaScript" in the search bar. Go to the Site Setting section, then click JavaScript and choose "Don't allow sites to use Javascript."
Warning! Most websites will not load without JavaScript — you will just see a white screen. Video players will not work on YouTube or Netflix.
We talked about the Internet without JavaScript in another article.
Do not use smartphones. The researchers at Cambridge University have found out that smartphones are easier to track and hack using browser fingerprinting. Smartphones' fingerprints never change, even if you reset your phone to default settings.
Use a virtual machine (VM). VM is a virtualization of acomputer system that is installed on topof the operating system. It helps to get rid of browser fingerprints since servers will collect information related to the VM.
The VM technical characteristics are emulated, and the real ones are hidden. For example, there is free software that allows you to install VMs. It is not much harder than installing the Windows OS. On top of that, you can use as many VMs as you want and change them when you want.
You can find the details, including Setup InstructionGuide, on the providers’ websites: VirtualBox (Windows, Linux, macOS, and Solaris), VMware Workstation Player (Windows and Linux), VMware Fusion (macOS), Hyper-V (Windows).
Use another device to access the Internet. For example, you can buy a second laptop for browsing the Internet, online shopping, and so on, and use your primary device for other purposes.
Use software to change browser fingerprint. For example, you can use the Multilogin service that helps create several accounts in the browser. Multilogin does not block browser fingerprints but replaces them with others. Multiloginhas two browsers –Mimic and Stealthfox.
- The Mimic browser. It is based on the Chromium engine and contains fingerprinting management technologies.
- The Stealthfox browser. It is based on the Firefox engine. It allows users to manage their fingerprints and choose what information the sites will get.
AdsPower is another option for fingerprint protection. It is an antidetect browser for creating multiple accounts on any platform. AdsPower allows you to configure fingerprinting and protect ads accounts from blocks. It also helps create numerous browser profiles and avoid online spying.
Conclusion
Browser fingerprinting is a method to identify users' devices on the Internet. It is used to detect fraudsters, personalize content and set up ads.
Block browser fingerprints if you want to keep your information safer. To do this, you can configure the browser, install a VM, and use Multilogin or special extensions that block fingerprints.