What Is VPN and How It Works? | Onlinesim
- Nov 29, 2022, 12:18 PM
- 12 minutes
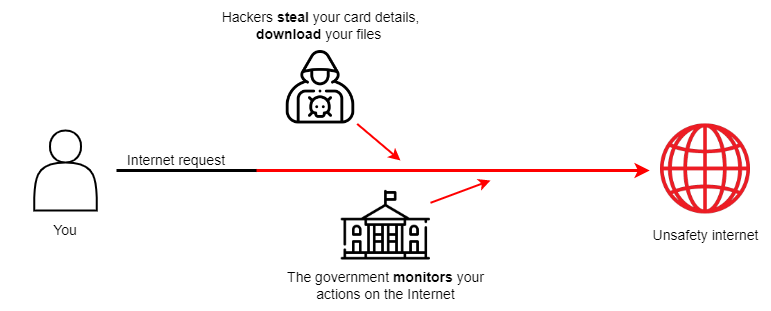
In 2021, an official website of the United States government published a report showing that Internet Service Providers collect data about devices, users' IPs, visited websites, etc., and sell it to online advertisers.
On top of that, hackers often steal personal information. For example, there were 1.4 million data theft incidents in the US in 2021.
One way to protect yourself from fraudsters and maintain the security of your data is to use a VPN. This article will tell you what a VPN is and how it works.
What Is a VPN?
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. This technology allows you to create one or more connections over a third-party network.
A VPN has a lot of benefits to offer, such as creating a private corporate network, bypassing restrictions, or secure transferring of files. In this article, we will discuss the principles of VPN operation and the key features (traffic anonymization and geo-restrictions bypassing).
Nowadays, people use VPN services to change their IP addresses and locations, bypass restrictions, and so on.
How Does a VPN Work?
All Internet users are assigned IP addresses (IP - Internet Protocol). When people connect to the Internet directly through an ISP's network, they get an IP address from the ISP's IP pool.
Providers must store and provide information on demand about who and when used the IP address and to which servers users were connected. They may also sell users' data to marketing agencies and analytic companies.
When using private networks, the user's provider will only see the connection with the servers. They are called entry points.
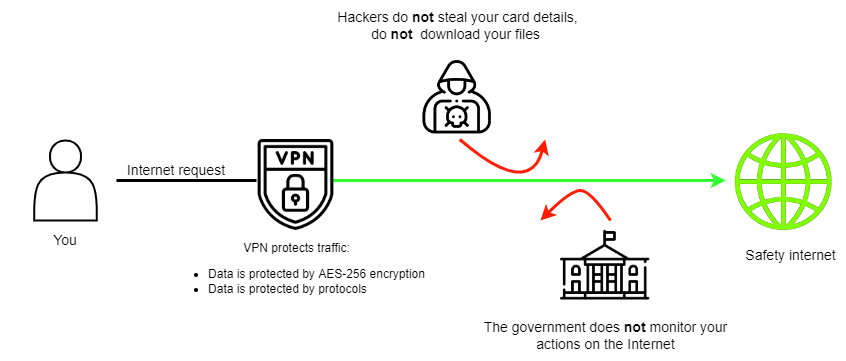
It works like this: when connecting to a VPN, the user's request is first routed to the VPN server. The VPN service creates a tunnel to encrypt the request and user's data. From there, the request goes to the destination website through a secure tunnel and returns the same way.
Therefore, even if someone gets access to confidential information, they will not be able to do anything without decrypting it first.
Moreover, a VPN changes users' location and IP addresses because its servers may be located in different countries. Different country — different IP.
Proxies come from devices, such as a peer's PC. And the majority of VPNs are located at datacenters.
Let's look at an example to understand how VPNs work. Suppose a person is invited to a party. Dress code — everyone should wear a mask so that no one can recognise each other. VPN is a mask but on the Internet. It hides your real IP and location, so remote servers, governments, and hackers cannot trace you.
What Protocol Types Does a VPN Use?
You can see in the picture that a VPN uses AES-256 encryption and different protocols.
AES-256 encryption. AES-256 is the most common and reliable encryption. Basically, encryption divides the data into several blocks that cannot be hacked.
Those operations are repeated several times and called "rounds." Every round has a unique key which is calculated out of the encryption key and incorporated in the calculations.
During encryption, every bit of data is replaced by another according to a pre-established table. Then a 4×4 matrix is used: row 2 — shift left 1 bit, row 3 — shift left 3 bit, row 4 — shift left 3 bit.
A new ciphertext block will be created when a bit has changed in a key or plaintext block.
To crack AES, you need to get all the unique round keys.
AES-256 is also called symmetric encryption because it uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt information. This is such a powerful algorithm that even a supercomputer would need more time to decrypt it than the universe's age.
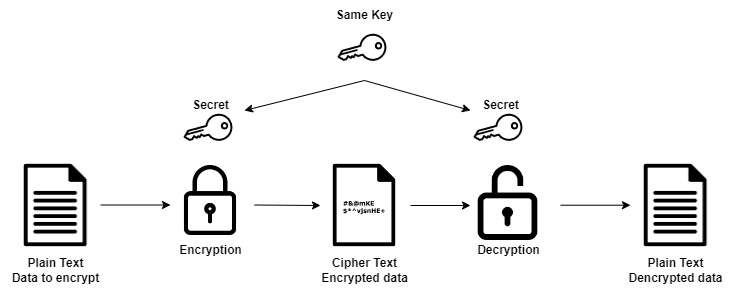
This is such a powerful algorithm that even a supercomputer would need more time to decrypt it than the universe's age.
Protocols: WireGuard, OpenVPN, L2TP / IPsec, , IKEv2 / IPsec. The first three are almost identical. The difference is in security and speed.
WireGuard is faster and more reliable than others. It uses modern cryptography and the UDP protocol to transfer data. And there are only 4000 lines in the code itself. This makes it easier to check for vulnerabilities and improve them.
OpenVPN, a universal open-source protocol, takes second place. OpenVPN code is longer than that of WireGuard, so finding and fixing vulnerabilities is more complicated. OpenVPN uses both TCP and UDP for data exchange.
The third place goes to L2TP/IPsec. L2TP does not encrypt traffic, so it is coupled with IPsec. L2TP uses UDP port 500, therefore, VPNs on this protocol sometimes fail: the port gets blocked by firewalls.
IKEv2 / IPsec is similar to the previous one but works on mobile devices.
On the one hand, it does not reduce the connection speed and is easy to configure. On the other hand, serious vulnerabilities were discovered in the PPTP protocol. Its authentication protocols are unreliable and have often been cracked during security analysis.
Types of VPNs
VPNs can be divided into two categories: for home and business users.
For home users
Personal VPNs. They are used to secure the internet connection and bypass firewalls and geo-restrictions.
Mobile VPNs. Mobile VPNs are the same as personal ones but work on smartphones.
For business users
Remote access VPNs. Employees use them to access the company's private network while traveling or working from home.
Site-to-site VPNs. While previous types of VPNs were designed to protect a single network, site-to-site VPNs connect different networks. For example, if a company has two offices in different countries, their networks can be linked together using a site-to-site VPN.
Why Do You Need a VPN?
Bypass restrictions. Sometimes governments block websites, so it is impossible to access them.
Maintain anonymity. Almost every website tracks users' real IP addresses. If a hacker breaks into the website, they will get all the IP addresses of the visitors.
Secure traffic. Suppose a hacker knows that a person is connected to the unsecured network; they will position themselves between the user's traffic and the server and intercept data. This type of cyberattack is called MITM (Man-in-the-middle.)
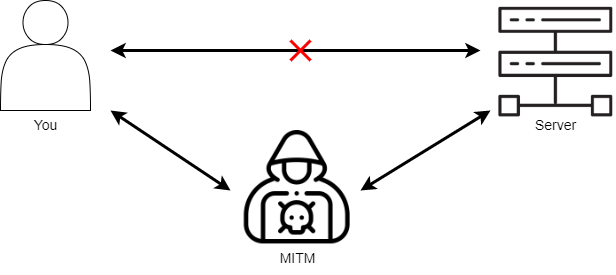
Connect to public networks. Public networks are found in subways, cafes, airports, and other public spaces. The problem of such networks is their weak security. Cybercriminals can hack and intercept users' outgoing traffic.
A VPN protects all your traffic, making it impossible to breach.
Create private corporate networks. If coworkers often exchange secret files, a hacker may want to break into and steal data.
Save money on shopping. The fact is that the prices of tickets or goods can vary from country to country. A VPN service changes your online location to the country with lower goods or ticket prices. Proxies are also suitable for these purposes.
Is It Legal to Use a Vpn?
Every country has different regulations regarding the legality of VPNs. For example, VPNs are completely legal in the USA, the UK, and Canada but banned in China.
Therefore, read the laws of your country before using a VPN.
You should not violate your VPN usage policy, such as by downloading copyrighted material.
Types of VPN Services
VPN services can work as a third-party application on a PC and smartphone or as a browser extension. VPNs differ in protocols but work along the same principles.
There are paid and free VPN services.
Differences between free and paid services.
They differ in the degree of protection, the number of functions, and the level of performance. Let's compare them.
| | Free VPN | Paid VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic protection | +/- | + |
| Geo-blocking bypass | +, not all VPNs | +, not all VPNs |
| Anonymity | Often sells users' data to advertisers, governments. | + |
| Encryption and reliable protocols | It depends on the service. They usually use PPTP protocol, which is easy to hack | + |
| Number of servers | Usually 1-10 servers in several countries | More than 100 servers |
| Bandwidth | Bandwidth is usually limited, the connection speed is reduced | Unlimited |
| Customer support | Usually does not respond to requests | Quick response; helps solve customers' problems |
Hola VPN is a free service to help bypass restrictions and protect your internet traffic. It has been operating since 2007, and the total number of users exceeds 220 million.
In 2015, 9 million Hola users’ addresses were used to carry out a DDoS attack against the website 8chan. People participated in cyberattacks without knowing it. It turned out that Hola was disclosing users' IDs, and hackers took advantage of this and stole customer addresses.
People were using a service that did not protect their traffic but only helping them bypass restrictions.
Paid services offer additional functions:
- Built-in firewall. A firewall is a shield between your device and the Internet. It blocks suspicious and phishing websites listed in the service database.
- DNS (Domain Name System) leak protection. DNS converts domain names to IP addresses and vice versa. Before you access any website, your device sends DNS queries to determine the IP address of the domain you are visiting.
When a DNS leak occurs, a hacker can get your real geographical location or the location of your internet provider and then your real IP address. VPNs protect you from data leaks because it uses other DNS servers to determine the host.
- Kill Switch. A kill switch feature automatically blocks outgoing traffic if your VPN connection drops out.
- Split Tunneling. A VPN service divides your internet traffic into two: one part of the traffic gets routed through a real IP address and the other through a virtual IP address. This feature can be helpful when accessing websites under the real IP.
Another advantage of paid VPNs is a money-back guarantee. It usually lasts for 30 days. It works like this: a person buys a VPN, but the service does not help to bypass restrictions or hide an IP address. The user contacts customer support and gets a refund.
What to Look Out for When Choosing a VPN?
The place of incorporation. It depends on the place of incorporation whether the company works with the government or not. For example, there is the Fourteen Eyes Alliance.
The alliance also includes NATO member countries:
And 🇮🇱 Israel, 🇸🇬 Singapore, 🇰🇷 South Korea, and 🇯🇵 Japan.
VPN services incorporated in these countries must hand over customer data to the governments on demand. They usually provide the following information:
- real IP address;
- session duration;
- device characteristics.
Therefore, it is better to choose services that are incorporated in other countries.
Number of servers. The more, the better. For example, if a company has few servers and a large number of users connected to them simultaneously, the servers may crash.
The load is evenly distributed when a VPN service has a vast network of servers.
Number of devices per account. The more, the better. You can use a VPN on multiple devices under one subscription.
The best scenario is if your VPN provider gives you instructions on how to install a VPN on a router. In this case, all connected devices will be granted the benefits of VPN protection.
No-Log Policy. A no-log policy means that the virtual private network provider does not collect any data. Only services outside the 14-Eyes Alliance can pursue a privacy-friendly policy.
Split Tunneling. One part of your internet traffic is routed through secure VPN servers, and the other goes through the standard connection. Thus, you can access the Internet under an IP assigned by your internet provider and an IP given by a VPN service.
Kill Switch. Kill Switch will not let your data leak if something happens to the company's servers.
AES-256 encryption. With AES-256 encryption, hackers will not be able to break into your traffic.
Built-in firewall. Built-in firewalls prevent you from falling into the trap of fraudsters or accidentally entering a phishing website.
DNS leak protection. With DNS leak protection, no one will know your real IP and location.
Live chat customer support. Live chat customer support will help you to solve any problems if any. Email-based support usually works slower.
Conclusion
A VPN helps create a secure and private network that protects you from fraudsters and phishing software. A VPN should be your pick if you need to bypass geo-blocking, maintain anonymity, access public networks, or create a corporate network.